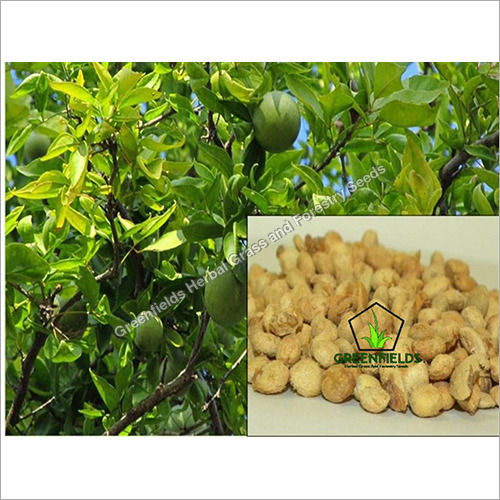
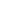
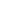
Aonla Fruit Seeds ( Emblica officinalis )
1300 INR/Kilograms
Product Details:
- Cultivation Type Other
- Variety Other
- Edible Yes
- Hybrid No
- Purity 100%
- Click to View more
X
Aonla Fruit Seeds ( Emblica officinalis ) Price And Quantity
- 1300 INR/Kilograms
- 5 Kilograms
Aonla Fruit Seeds ( Emblica officinalis ) Product Specifications
- No
- 100%
- Yes
- Other
- Other
Aonla Fruit Seeds ( Emblica officinalis ) Trade Information
- 10000 Kilograms Per Year
- 5 Days
- Free samples available with shipping and taxes paid by the buyer
- PP bags
- All India
Product Description
Enter Buying Requirement Details

 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese