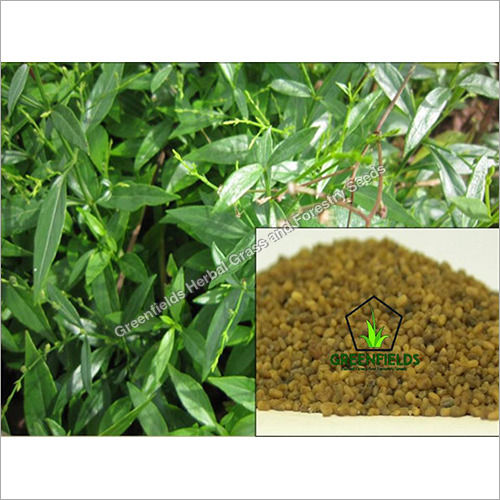
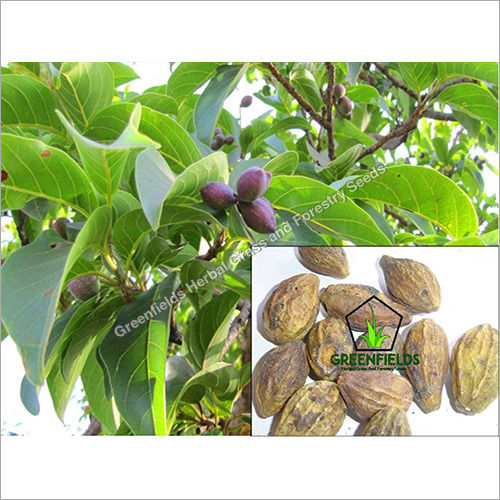
Yellow Akarkara Medicinal Seeds ( Acmella Oleracea)
Product Details:
- Type Dried Herbs
- Storage Instructions other
- Click to View more
Yellow Akarkara Medicinal Seeds ( Acmella Oleracea) Price And Quantity
- 5Kg Kilograms
- 650 INR
Yellow Akarkara Medicinal Seeds ( Acmella Oleracea) Product Specifications
- other
- Dried Herbs
Yellow Akarkara Medicinal Seeds ( Acmella Oleracea) Trade Information
- 1000 Kilograms Per Year
- 5 Days
- Free samples available with shipping and taxes paid by the buyer
- PP bags
- All India
Product Description
Yellow Akarkara Medicinal Seeds ( Acmella Oleracea)
- Last modified on: 08 Apr 2014
- Scientific Name:- Acmella oleracea
- Shape:- Oval
- Size:-1.5 cm
- Color: -Brown
- Usage: Germination
- Age: Fresh
- Origin: India
- Packing: -5, 10,20,25,50 (P/P)
- Availability :- Throughout the year
Details:-
- Common name: Akarkara
- Hindi Name: Akarkara
- Botanical name: Acmella oleracea
- Family : Asteraceae
Acmella oleracea (syn. Spilanthes oleracea, S. acmella) is a species of flowering herb in the family Asteraceae. Common names include toothache plant and paracress. In Brazil it is called jamb. Its native distribution is unclear, but it is likely derived from a Brazilian Acmella species. It is grown as an ornamental and it is used as a medicinal remedy in various parts of the world. A small, erect plant, it grows quickly and bears gold and red inflorescences. It is frost-sensitive but perennial in warmer climates.
For culinary purposes, small amounts of shredded fresh leaves are said to add a unique flavour to salads. Cooked leaves lose their strong flavour and may be used as leafy greens. Both fresh and cooked leaves are used in dishes such as stews in northern Brazil, especially in the state of Par. They are combined with chilis and garlic to add flavor and vitamins to other foods.
The flower bud has a grassy taste followed by a strong tingling or numbing sensation and often excessive salivation, with a cooling sensation in the throat. The buds are known as "buzz buttons Szechuan buttons sansho buttons, and electric buttons . In India, they are used as flavoring in chewing tobacco.
A concentrated extract of the Spilanthes plant identified as Jambu is used as a flavoring agent in many countries worldwide. EFSA and JECFA reviewed a feeding study in rats conducted by Moore et al and both authorities recognized that the no adverse effect level for spilanthol was 572 mg/kg b.w./day, yielding a safe dose of spilanthol of 1.9 mg/kg b.w./day, or 133.5 mg/70-kg male/day, 111 mg/58-kg female/day, or 38 mg/20-kg child/day.
The use of jambu extract as a food flavor is described as having an odor of citrus, herbal, tropical or musty odor, and its taste can be pungent, cooling, tingling, numbing, or effervescent. Thus, as described, the flavor use of jambu extract includes the ability induce a mouth-watering sensation in the oral cavity and the ability to promote the production of saliva. Spilanthol, the major constituent of jambu extract, is responsible for the perception of a mouth-watering flavor sensation, as well as the ability to promote salivation as a sialogogue, perhaps through its astringent action or its pungent taste in the oral cavity.
This plant prefers well-drained, black (high organic content) soil. If starting outdoors, the seeds should not be exposed to cold weather, so start after last frost. Seeds need direct sunlight to germinate, so don't bury them.
Medicinal uses
A decoction or infusion of the leaves and flowers is a traditional remedy for stammering, toothache, and stomatitis.
An extract of the plant has been tested against various yeasts and bacteria and was essentially inactive. It has been shown to have a strong diuretic action in rats.
Related product:
1.Shatavari white seeds
2 Ashwagandha seeds
3. Kalmegh seeds
4. Harra seeds
5. Gataran seeds
6. Amaltash seeds
7. Munga seeds.

 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese